level0
base64解码
S1JZUFRPTklTR1JFQVQ=
|
|
\|/
KRYPTONISGREAT
level1
差点儿没找着文件,真抽象。
krypton1@bandit:/krypton/krypton1$ ll
total 16
drwxr-xr-x 2 root root 4096 Apr 23 18:05 ./
drwxr-xr-x 8 root root 4096 Apr 23 18:05 ../
-rw-r----- 1 krypton1 krypton1 26 Apr 23 18:05 krypton2
-rw-r----- 1 krypton1 krypton1 882 Apr 23 18:05 README
krypton1@bandit:/krypton/krypton1$ cat README
Welcome to Krypton!
This game is intended to give hands on experience with cryptography
and cryptanalysis. The levels progress from classic ciphers, to modern,
easy to harder.
Although there are excellent public tools, like cryptool,to perform
the simple analysis, we strongly encourage you to try and do these
without them for now. We will use them in later excercises.
** Please try these levels without cryptool first **
The first level is easy. The password for level 2 is in the file
'krypton2'. It is 'encrypted' using a simple rotation called ROT13.
It is also in non-standard ciphertext format. When using alpha characters for
cipher text it is normal to group the letters into 5 letter clusters,
regardless of word boundaries. This helps obfuscate any patterns.
This file has kept the plain text word boundaries and carried them to
the cipher text.
Enjoy!
krypton1@bandit:/krypton/krypton1$ cat krypton2 | tr [A-Z] [N-ZA-M]
LEVEL TWO PASSWORD ROTTEN
krypton1@bandit:/krypton/krypton1$
就一个移位密码
level2
还是一个移位密码
krypton2@bandit:/tmp/krypton2$ cat /etc/issue
Ubuntu 22.04.2 LTS \n \l
krypton2@bandit:/tmp/krypton2$ /krypton/krypton2/encrypt /etc/issue
krypton2@bandit:/tmp/krypton2$ cat ciphertext
GNGZFGXFEZXkrypton2@bandit:/tmp/krypton2$
因此
krypton2@bandit:/tmp/krypton2$ cat /krypton/krypton2/krypton3 | tr [A-Z] [O-ZA-N]
CAESARISEASY
krypton2@bandit:/tmp/krypton2$
level3
提示是统计,那就知道了
krypton3@bandit:/krypton/krypton3$ cat found{1..3} | tr -cd '[:alpha:]' | fold -w1 | sort | uniq -c | sort -nr
456 S
340 Q
301 J
257 U
246 B
240 N
227 G
227 C
210 D
132 Z
130 V
129 W
86 M
84 Y
75 T
71 X
67 K
64 E
60 L
55 A
28 F
19 I
12 O
4 R
4 H
2 P
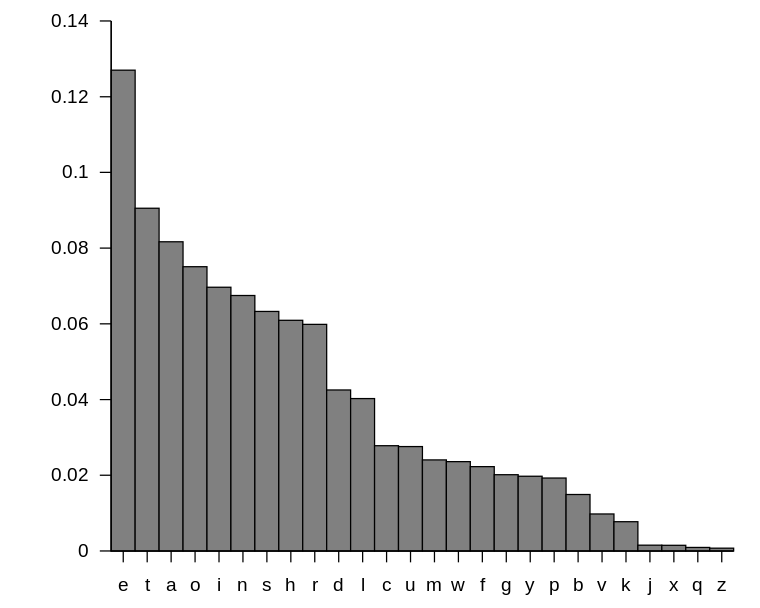 然后这儿有个这玩意,大概能看出来
然后这儿有个这玩意,大概能看出来
但是不完全准,来回试试基本上就可以了
krypton3@bandit:/krypton/krypton3$ cat krypton4 | tr 'KSVWBDGIXMNYQUCAJ' 'WELDOHNVFURPASIBT'
WELLD ONETH ELELE LFOUP RASSW OPDIS XPUTE krypton3@bandit:/krypton/krypton3$
比如说你猜krypton里面有password,然后猜一下就行。
level4
直接看wp了反正是。。。
cleartext
这里有个破解这种密码的中文参考,可以看一看
level5
这回,搜了个脚本儿。。。
自己写是真不会。。。
当然,首先需要一点点小的命令
cat /krypton/krypton5/found{1..3} | tr -d '[:space:]' > output.txt
然后跑脚本
import string
# 加载密文
with open('output.txt', 'r') as f:
cipher = f.read()
#coding=utf-8
#-*- coding:utf-8 –*-
def c_alpha(cipher): # 去掉非字母后的密文
cipher_alpha = ''
for i in range(len(cipher)):
if (cipher[i].isalpha()):
cipher_alpha += cipher[i]
return cipher_alpha
# 计算cipher的重合指数
def count_CI(cipher):
N = [0.0 for i in range(26)]
cipher = c_alpha(cipher)
L = len(cipher)
if cipher == '':
return 0
else:
for i in range(L): #计算所有字母的频数,存在数组N当中
if (cipher[i].islower()):
N[ord(cipher[i]) - ord('a')] += 1
else:
N[ord(cipher[i]) - ord('A')] += 1
CI_1 = 0
for i in range(26):
CI_1 += ((N[i] / L) * ((N[i]-1) / (L-1)))
return CI_1
# 计算秘钥长度为 key_len 的重合指数
def count_key_len_CI(cipher,key_len):
un_cip = ['' for i in range(key_len)] # un_cip 是分组
aver_CI = 0.0
count = 0
for i in range(len(cipher_alpha)):
z = i % key_len
un_cip[z] += cipher_alpha[i]
for i in range(key_len):
un_cip[i]= count_CI(un_cip[i])
aver_CI += un_cip[i]
aver_CI = aver_CI/len(un_cip)
return aver_CI
## 找出最可能的前十个秘钥长度
def pre_10(cipher):
M = [(1,count_CI(cipher))]+[(0,0.0) for i in range(49)]
for i in range(2,50):
M[i] = (i,abs(0.065 - count_key_len_CI(cipher,i)))
M = sorted(M,key = lambda x:x[1]) #按照数组第二个元素排序
for i in range(1,10):
print (M[i])
F = [
0.0651738, 0.0124248, 0.0217339,
0.0349835, 0.1041442, 0.0197881,
0.0158610, 0.0492888, 0.0558094,
0.0009033, 0.0050529, 0.0331490,
0.0202124, 0.0564513, 0.0596302,
0.0137645, 0.0008606, 0.0497563,
0.0515760, 0.0729357, 0.0225134,
0.0082903, 0.0171272, 0.0013692,
0.0145984, 0.0007836
] # 英文字符频率。
cipher_alpha = c_alpha(cipher)
print ("秘钥长度为:")
pre_10(cipher)
然后有如下输出:
krypton5@bandit:/tmp/krypton5$ python3 test.py
秘钥长度为:
(9, 0.017139818147855056)
(36, 0.017203685000228598)
(18, 0.01721992202177322)
(27, 0.017472532653033286)
(45, 0.0176209079041227)
(33, 0.020346335439459143)
(48, 0.020422875620895405)
(24, 0.020464673333004946)
(30, 0.02051347672724485)
这个也看了一下wp,九位密码是准的,但是程序输出的密钥不准,不知为什么。
密钥是 keylength, 答案是 RANDOM
level6
这个还是那个维吉尼亚的变形,没有太难。
ciphertext = 'PNUKLYLWRQKGKBE'
key = 'EICTDGYIYZKTHNSIRFXYCPFUEOCKRN'
for c, k in zip(ciphertext, key):
p = ord('A') + ((ord(c) - ord(k)) % 26)
print(chr(p), end='')
print()
最后密码如下
LFSRISNOTRANDOM
ref
这些东西感觉知道原理就差不多了,自己写实在是没意思而且有些困难。
也有不少人写脚本分析,但是感觉那些脚本分析出来的也不是很准,还是需要人工来看,反正有兴趣的可以搜搜。
去网上看了看发现别人也是用工具,自己分析真是过于无聊了。 ref3